Workers
PHP-FPM uses pools and worker processes to handle PHP requests efficiently. Each site has its own PHP-FPM pool, which defines how resources like CPU and RAM are allocated. To monitor and optimize performance, navigate to Site > Processes, where you can view real-time CPU and RAM usage for each process. This information helps you determine the optimal number of workers your server can handle, ensuring smooth operation under varying loads.
On-Demand Workers
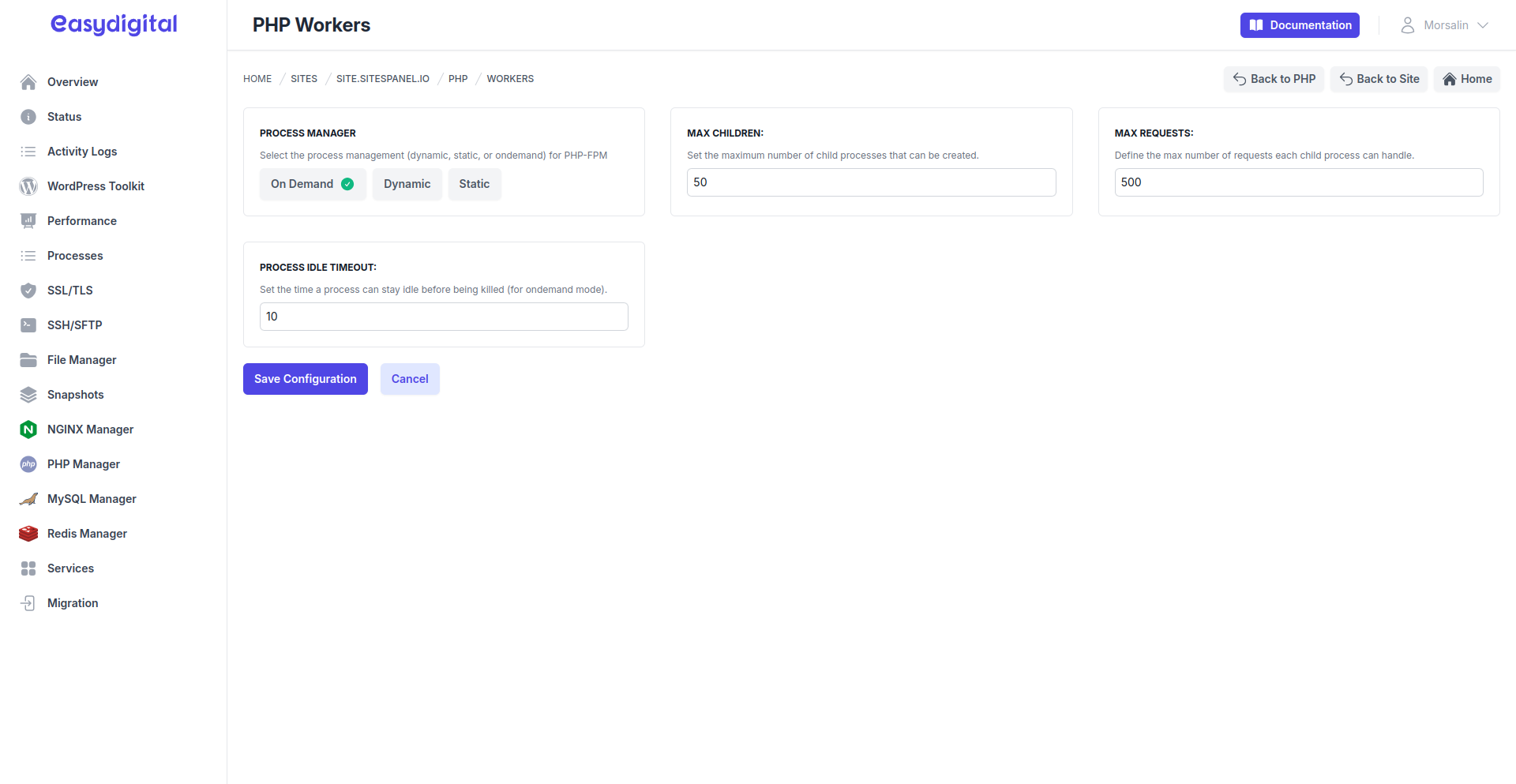 |
|---|
Field | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Max Children | The maximum number of child processes that can be created to handle requests. | Integer |
Max Requests | The maximum number of requests a single worker process can handle before being terminated and replaced. | Integer |
Process Idle Timeout | The duration a worker process remains idle before it is terminated to free resources. | Integer (Seconds) |
Dynamic Workers
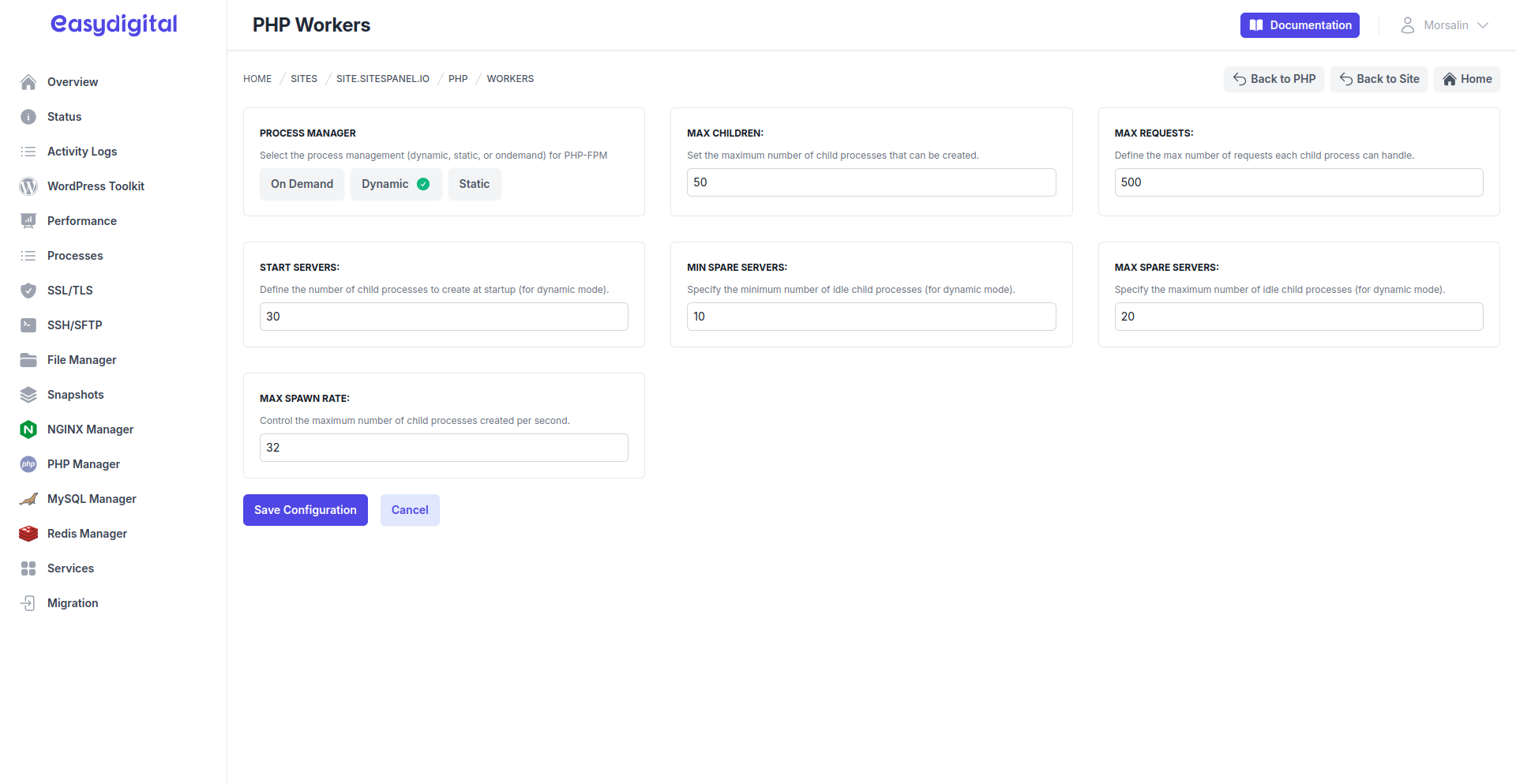 |
|---|
Field | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Max Children | The maximum number of child processes that can be created to handle requests. | Integer |
Max Requests | The maximum number of requests a single worker process can handle before being terminated and replaced. | Integer |
Start Servers | The number of child processes created when the pool starts. | Integer |
Min Spare Servers | The minimum number of idle processes to keep available to handle bursts of traffic. | Integer |
Max Spare Servers | The maximum number of idle processes to maintain, terminating any excess to conserve resources. | Integer |
Max Spawn Rate | The maximum rate at which new processes are created to handle incoming requests. | Integer |
Static Workers
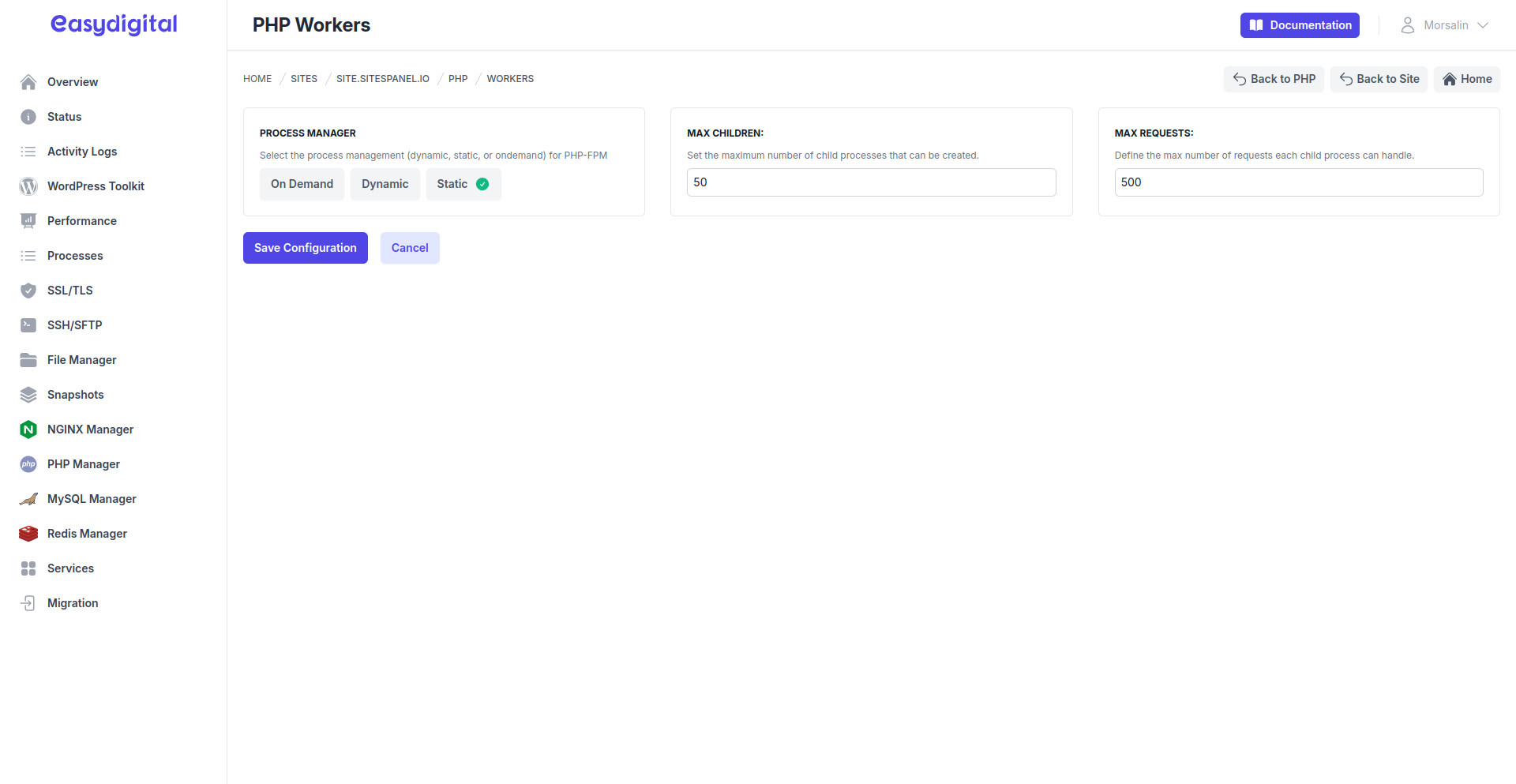 |
|---|
Field | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Max Children | The exact number of worker processes to create and maintain at all times. | Integer |
Max Requests | The maximum number of requests a single worker process can handle before being terminated and replaced. | Integer |